Zinc Deficiency: What You Should Know
What is Zinc Deficiency?
Zinc deficiency or hypozincemia is caused by lack of zinc in the diet. It can also be caused by other diseases such as liver disease, cystic fibrosis, and even congenital abnormalities.
According to the studies and surveys done by several world health organizations, about 31% of the entire population is at risk of zinc deficiency. In fact, zinc deficiency is one of the leading risk factors for disease in developing countries.

Congenital Zinc Deficiency
What Are the Main Causes of Zinc Deficiency?
The primary causes of zinc deficiency or hypozincemia are the following:
- Inadequate zinc in the diet.
- Diseases or conditions that disrupt proper digestion. Diarrhea and malabsorption is one of them.
- Physiological states such as during pregnancy, or during the early stage of growth of infants and young children, which require increased intake of zinc.
- Disease in kidney or liver.
- After undergoing bariatric surgery (removal of parts of the stomach or intestines to induce weight loss).
- Heavy metal exposure to zinc. For example, people living near zinc smelters.
- Tartrazine (artificial orange-yellow dye used commonly as food coloring) can disrupt the body's ability to absorb zinc.
- Vitamin A and D deficiency. Studies have shown that the body's ability to maintain zinc levels is dependent on A and D vitamins.

Acrodermatitis Enteropathica
What Are the Symptoms of Zinc Deficiency?
- Eczema, skin rashes, and many other skin conditions.
- Diarrhea and pneumonia.
- Acne.
- Vision loss and poor sense of smell and taste – Zinc is vital for the development of our five senses.
- Anorexia (prolonged loss of appetite) – Zinc is an appetite stimulator.
- Low testosterone production in men.
- Dysmenorrhea.
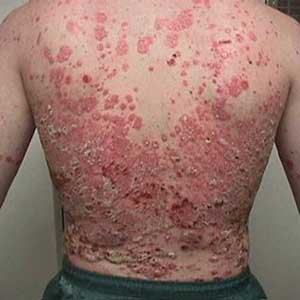
Scalp Psoriasis
How Do You Treat Zinc Deficiency?
Zinc deficiency can be treated by taking dietary zinc supplements, or by eating foods that are rich and fortified with zinc.
What Are Foods Rich in Zinc?
Animal foods are actually richer in zinc than plant foods.
Below are the top 10 foods that are rich in zinc. Note that the current daily value for zinc is 15 mg for adults and children aged 4 and above.
1. Oysters
Oysters contain the most zinc than any other foods. Cooked oysters can typically provide 74 mg of zinc per 100 g serving. This already accounts for almost 500% Daily Value.

Remember that oyster is a high cholesterol food and must be taken in moderate amounts only.
2. Wheat Germ

Wheat germs are usually sold toasted and packed in jars. Sprinkle them on top of foods like rice, vegetables, and salads. Toasted wheat germ provides 17 mg of zinc per 100 g serving, which is still more than 100% Daily Value.
3. Calf Liver

Animal livers are not only packed with nutrition. They are also an excellent source of zinc. A calf liver has the most zinc, with 12 mg of zinc per 100 g serving accounting for 81% Daily Value.
4. Roast Beef
Just like liver, roast beef is also loaded with zinc. Make sure that you go with the low-fat kind. It contains about 10 mg of zinc per 100g serving. That's 70% Daily Value.
5. Roasted Squash and Pumpkin Seeds
Pumpkin and squash seeds contain about 10 mg of zinc per 100 g serving, also a 70% Daily Value.
Squash or pumpkin seeds are popular in East Asia and the Middle East. So if you can't find these in your local supermarket, you'll most likely be able to buy them in East Asian or Middle Eastern specialty stores.
Otherwise, you can also save any squash and pumpkin seeds you have and then have them roasted by yourself.
6. Dried Watermelon Seeds
Just like pumpkin and squash seeds, watermelon seeds also contain 10 mg of zinc per 100 g serving (70% Daily Value).
They are also popular in the Middle East and East Asia so you can find them in specialty stores.
Watermelon seeds can be eaten raw. You can shell them or eat them whole.
7. Cocoa or Dark Chocolate
Chocolate or cocoa are not just potent antioxidants. They also contain high amounts of zinc. Make sure it's dark chocolate! Dark chocolate can provide 9.6 mg of zinc per 100 g serving (64% Daily Value). Milk chocolates have lower zinc levels providing only about 2.3 mg per 100 g serving (15% Daily Value).
8. Lamb (Mutton)
Depending on the quality of the meat, lamb can provide anywhere from 4.2 to 8.7 mg of zinc per 100 g serving. That's 28% to 58% Daily Value.
9. Crab
Any kinds of crabs are good sources of zinc. Crabs can provide 7.6 mg of zinc per 100 g serving (51% Daily Value).
10. Peanuts
Peanuts are great sources of zinc. The amount of zinc varies depending on the type of peanut.
Oil-roasted peanuts will provide 6 mg of zinc per 100 g serving (40% Daily Value). Dry roasted peanuts will only provide half as much zinc at 3 mg per 100 g serving. That's 20% Daily Value.
What about Zinc for Vegetarians?
First of all, plant foods such as cereals, nuts, seeds, and legumes, contain phytate (phytic acid). In biochemistry, phytic acid readily binds with metals to form salts. In other words, phytic acid will inhibit the body's absorption of zinc.

Cabbage is known as the vegetable with the most zinc by weight.
Therefore, vegetarians may need more than the recommended daily allowance (15 mg) of zinc every day. Major sources of zinc in plants include sea vegetables, baked beans, soy foods, peanuts, sesame or pumpkin seeds, and peas.
Reprint Rights: You may reprint this article within your website, blog, or newsletter as long as the entire article remains the same as well as the “About the Author” box.



 Junji Takano is a Japanese health researcher involved in investigating the cause of many dreadful diseases. In 1968, he invented PYRO-ENERGEN, the first and only electrostatic therapy machine that effectively eradicates viral diseases, cancer, and diseases of unknown cause.
Junji Takano is a Japanese health researcher involved in investigating the cause of many dreadful diseases. In 1968, he invented PYRO-ENERGEN, the first and only electrostatic therapy machine that effectively eradicates viral diseases, cancer, and diseases of unknown cause.


